July 02, 2025
Tag:
1 Preface
The total acid in condiments usually refers to various organic acids such as lactic acid, acetic acid, citric acid and succinic acid they contain. The appropriate presence of organic acids has a certain effect on the flavor of condiments. The GB 12456-2021 National Food Safety Standard for the determination of total acid in food, revised in 2021, added the third method of potentiometric titration. This scheme formulated based on the national standard can be equipped with a 16-position automatic sampler, which can be automatically cleaned and tested. The experimental process is simple, time-saving and labor-saving. It also avoids the subjective error caused by manual judgment of the endpoint and is the preferred choice for detecting the total acid index of food.
2. Instruments and equipment
2.1 Instruments
JH-T6 fully automatic potentiometric titrator, composite PH electrode.
2.2 Reagents
Sodium hydroxide titrant (0.1 mol/L)
3 Experimental Methods
3.1 Experimental Procedures
(1) Preparation: Calibrate the PH electrode with buffer solutions of PH=4.01, 6.86, and 9.18.
(2) Test Accurately transfer 1ml of the original vinegar sample with a 1mL pipette and place it in a titration cup. Add 50ml of deionized water (ensuring that the solution height covers the electrode), place it on the potentiometric titration stand, start stirring to ensure uniform mixing of the sample, insert the electrode and titration head, and after the potential stabilizes, start the prepared method. Titrate with the calibrated sodium hydroxide (0.100mol/L) standard solution until PH=8.2, record the volume of sodium hydroxide standard solution consumed, and conduct a blank test simultaneously.
The operation steps for five-spice passion vinegar, soy sauce and cooking wine (transfer 20mL of volume with a 20mL pipette) are the same as above.
3.2 Parameter Settings
| Titration mode | endpoint titration | Equilibrium potential before titration 6mV |
6mV |
| The stirring speed |
7 |
the final volume |
10mL |
| Fast drop volume: |
0.2mL |
slow drop volume |
0.02mL |
| Fast drop potential equilibrium time |
4s |
fast drop equilibrium potential |
1mV |
| Slow drop potential equilibrium time |
4s |
slow drop equilibrium potential |
1mV |
| Titration endpoint |
8.3 |
re-control value 7.3 (with a delay of 10 seconds) |
4. Results and Discussion
4.1 Experimental Results
|
Sample name |
Sample compilation number |
Concentration of titrant (mol/L |
Sampling volume (mL |
Titration volume V1 (mL |
Blank volume V0 (mL) | Total acid content (g/100mL) |
Total acid content (g/100mL |
RSD(%) |
|
Original brewed vinegar |
1 |
0.1580 |
1 |
5.070 |
0.02 |
4.787 |
4.8087 |
0.3984 |
|
2 |
5.085 |
4.802 |
||||||
|
3 |
5.110 |
4.825 |
||||||
|
Five-grain and hundred-spice vinegar |
1 |
1 |
5.470 |
5.167 |
5.1637 |
0.118 |
||
|
2 |
5.460 |
5.157 |
||||||
|
3 |
5.470 |
5.167 |
||||||
|
Scallion, ginger and cooking wine |
1 |
20 |
5.140 |
3.640 |
3.6403 |
0.3984 |
||
|
2 |
5.120 |
3.626 |
||||||
|
3 |
5.160 |
3.655 |
||||||
|
Pilot production finished product Soy sauce |
1 |
1 |
1.020 |
1.422 |
1.4307 |
1.1247 |
||
|
2 |
1.040 |
1.450 |
||||||
|
3 |
1.020 |
1.420 |
Calculation formula
X(g /100mL) =  ×100
×100
In the formula:
V1 is the volume of titrant consumed by the sample. V0 represents the volume of the titrant consumed blank.
V is the volume of the sample weighed.
4.2 Atlas
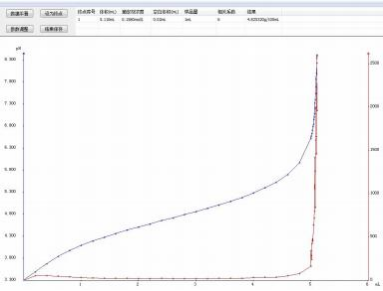
4.3 Conclusion
The JH-T6 fully automatic potentiometric titrator is used to determine the total acid content of condiments. The results have good repeatability and are all within its standard range. Moreover, it can be connected to an automatic sampler, which greatly increases the efficiency. This instrument fully meets the requirements for determining the total acid content of condiments.
References
[1]GB/T 12456-2021. Determination of Total Acid in food [S].


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
+86 15021993094


