July 04, 2025
Tag:
1 Preface
In addition to lycopene, tomato sauce also contains B vitamins, dietary fiber, minerals, proteins and natural pectin, etc. Compared with fresh tomatoes, the nutrients in tomato sauce are more easily absorbed by the human body. Adding an appropriate amount of sodium chloride to food can improve its taste. The amount of sodium chloride added directly affects the flavor of food. Therefore, the determination of chloride content has become one of the items that many foods must test. The National standard of the People's Republic of China, "GB 5009.44-2016 Determination of Chloride in Food", clearly stipulates the method for determining the chloride content in food. In this paper, the content of chloride in tomato sauce was determined by using a potentiometric titrator according to the method in the standard. The operation is simple and the results are accurate.
2. Instruments and reagents
2.1 Instruments
JH-T6 fully automatic potentiometric titrator, silver composite electrode
2.2 Reagents
Silver nitrate standard solution (0.02mol/L), acetone, nitric acid solution (1+3)
3 Experimental Methods
3.1 Experimental Procedures
Accurately weigh 5g of the sample into a 100mL volumetric flask, add 50mL of water and mix evenly. Ultrasonicate for 20 minutes, add water to make up to the mark, mix well, and filter. Accurately transfer an appropriate amount of filtrate (the volume of the sample solution to be taken depends on the chloride content of the sample) into a titration cup, add 5mL of nitric acid solution, 25mL of acetone, and 30mL of pure water, stir evenly, and then titrate to the endpoint with 0.02mol/L silver nitrate titrant. At the same time, conduct a blank test.
3.2 Parameter Settings
| Titration mode: |
Dynamic titration |
stirring speed: |
5 |
| Electrode equilibrium time: |
20s |
pre-stirring time: |
6s |
| Electrode equilibrium potential: |
1mv |
titration speed: | standard |
| Minimum addition volume: |
0.05mL |
Pre-titration addition volume: |
6mL |
| Final volume: |
10mL |
Pre-titration stirring time: |
20s |
| Potential spike: |
100 |
Correlation coefficient: |
177.25 |
4. Results and Discussion
4.1 Experimental Results
|
Sample name |
Concentration of titrant (mol/L |
Sample quantity (mL |
Liquid volume taken (mL |
Titration volume (mL |
Chloride ion (% |
Average value (% |
|
Tomato sauce |
0.02084 |
5.04357 |
2 |
9.798 |
6.96 |
7.01 |
|
9.816 |
6.97 |
|||||
|
10.009 |
7.11 |
4.2 Calculation Formula:
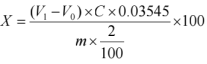
X- The content of chloride ions in the sample, expressed as a percentage (%);
V1- Volume of silver nitrate standard titration solution consumed in titrating the sample dilution solution, measured in milliliters (mL); V0- Volume of silver nitrate standard titration solution consumed blank, unit: milliliters (mL);
C - Concentration of silver nitrate standard titration solution, unit: moles per liter (mol/L).
4.3 Map
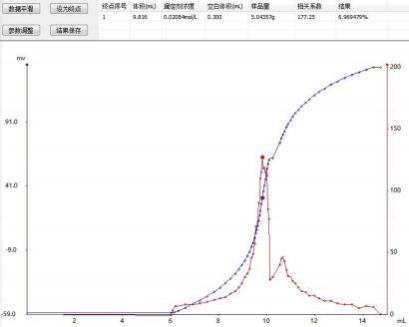
4.4 Conclusion
The result data shows that the potentiometric titration method for determining the chloride ion content in tomato sauce has good repeatability, and the absolute difference of the determination results meeting the national standard requirements does not exceed 5% of the arithmetic mean. The instrument can automatically control the titration process, determine the endpoint and process data, reducing the error caused by naked-eye determination of the endpoint. It features rapidity and accuracy.
References
[1] GB/T 5009.44-2016 National Food Safety Standard - Determination of Chloride in Food [S].


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
+86 15021993094


