July 04, 2025
Tag:
I. Preface
The standard for chloride ion content in compound fertilizers is one of the important guiding standards for the production and application of chemical fertilizers. Adhering to the standard regulations and ensuring the quality and safe use of compound fertilizers is the key to safeguarding the stable and healthy development of agricultural production. In this experiment, a T960 potentiometric titrator was used to select fertilizers from a certain manufacturer to observe the content of chloride ions. The content of chloride ions is determined by the automatic potentiometric titration method in Appendix 2 of GB/T 15063-2020 Compound Fertilizer. The principle is to boil water to extract the chloride ions in the sample, use a silver electrode as the indicator electrode, and titrate the chloride ions in the sample with silver nitrate titrant. The potential leap of the automatic potentiometric titrator is taken as the indicator endpoint. The content of chlorine examples is calculated based on the volume and concentration of the consumed silver nitrate titrant.
Ii. Instruments and Reagents
2.1 Instruments
JH-T6 fully automatic potentiometric titrator, composite silver electrode, electric heating plate, 250mL beaker, 250mL volumetric flask, surface dish, etc
2.2. Reagents
0.1mol/L silver nitrate titrant, deionized water
Iii. Experimental Methods
3.1 Experimental Process
3.3.1 Sample preparation process
The sample preparation process is in accordance with the determination method of compound fertilizer in GB/T 15063-2020. The specific operation is as follows:
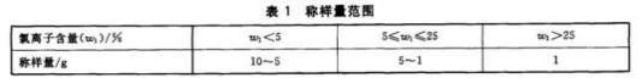
Weigh the appropriate weight of the sample according to Table 1 (for example, if the chloride ion content of the No. 1 compound fertilizer sample is 2.5% < 5%, the sampling amount should be between 10 and 5g), accurately to 0.0001g, place it in a 250mL beaker, add 100mL of deionized water, heat slowly to boiling, and continue to boil gently for 10 minutes. Cool to room temperature, transfer the solution to a 250mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark, and mix well. Dry filter, discard the initial part of the filtrate, collect the filtrate and wait for testing.
3.3.2 Process of chloride ion content determination
Accurately draw 10 ml of the filtrate into the titration cup with a 10mL pipette, add 5mL of (1+1) nitric acid solution, and add 40mL of deionized water to make the total volume of the solution 50mL. Titrate with the calibrated silver nitrate until the potential jump endpoint. At the same time, conduct a blank experiment (add 50 ml of deionized water and 5mL of nitric acid solution, and titrate with equal volume until the endpoint).
3.2 Instrument Parameters
The parameter Settings of the JH-T6 fully automatic potentiometric titrator are shown in Table 1
Table 1 Parameter Settings of Titrator
| Titration type: Dynamic titration | Method Name: Determination of Chloride Ions in Fertilizers by Silver Nitrate Method | ||
| Burette volume: 10mL | Sample measurement unit: g | ||
| Working electrode: Composite silver electrode | Reference electrode: None | ||
| Stirring speed: 7. | Pre-stirring time: 5 seconds | ||
| Electrode equilibrium time: 4 s | electrode equilibrium potential: 1mv | ||
| Titration speed: Equilibrium potential | before standard titration: 6mv | ||
| Minimum addition volume: 0.02mL | Potential spike: 800 | ||
| Correlation coefficient: 86.625 | pre-control value: -50 | ||
| Titrant name: Silver nitrate | Theoretical concentration: 0.1028 |
Iv. Results and Discussion
4.1 Experimental Results
The samples were tested and the experimental results are shown in Table 2
Table 2 Test Results of Chloride Ion Content
| Sample name |
Sampling volume (g |
c(AgNO3)/ mol/L |
The aspirated volume during titration is V1/mL | Titrate the sample volume V2/mL |
Titrate the blank volume Product V/mL |
Chlorine content (%) |
Average value (%) |
RSD(%) |
|
# 1 Reunion fat |
5.0862 |
0.1028 |
10 |
1.464 |
0.02 |
2.587 |
2.594 |
0.248 |
|
1.470 |
2.597 |
|||||||
|
1.470 |
2.599 |
|||||||
|
No. 2 compound mixing fat |
2.0199 |
10 |
4.889 |
21.961 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
4.875 |
21.898 |
|||||||
|
No. 3 needle-like fat |
2.0109 |
10 |
5.167 |
23.319 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
5.183 |
23.392 |
|||||||
|
4#氮鉀 肥 |
1.0937 |
10 |
6.089 |
50.630 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
6.083 |
50.506 |
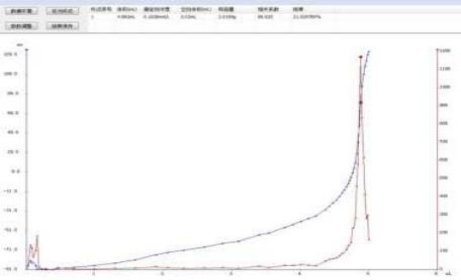
4.2 Titration chromatogram
4.3. Conclusion
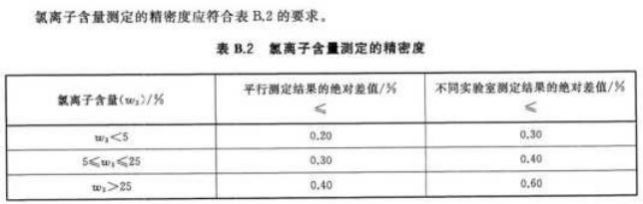
This test determined the chloride content in the fertilizer through an automatic potentiometric titrator, and the test results met the precision requirements in the above table. Moreover, the use of instruments for judgment reduces human errors and greatly improves the accuracy of experiments. Potentiometric titration is a good choice for detecting the content of such samples.
V. Precautions
At present, the reference standards for testing the chloride content in fertilizers are GB/T 24890-2010 - Determination of Chloride Ion Content in Compound Fertilizers and GB/T 15063-2020 - Compound Fertilizers, and the 2020 version is universal.


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
+86 15021993094
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight July 2025
Pharma Sources Insight July 2025


