June 06, 2025
Tag:
1. Preface
Aspartan (C14H18N2O50), scientifically known as aspartan, is a non-carbohydrate artificial sweetener. When used as a sweetener, it does not cause a significant increase in blood sugar. Therefore, it is mainly used to make foods suitable for diabetic patients and can help lower blood sugar. However, studies have shown that Excessive intake may pose risks such as abnormal brain nerves and brain tumors. This plan utilizes the T960 fully automatic potentiometric titrator to determine the content of the active ingredient of the drug through non-aqueous titration with perchloric acid, to see if the content index meets the requirements for mass production. This scheme has a simple experimental process, takes less time, and avoids the subjective error caused by manual determination of the endpoint. It is a good choice for detecting the content of this type of drug.
2 Instruments and equipment
2.1 Instruments
JH-T7 fully automatic potentiometric titrator, composite PH electrode.
2.2 Reagents
Perchloric acid standard solution (0.1 mol/L), glacial acetic acid, anhydrous formic acid.
3 Experimental Methods
3.1 Experimental Procedures
Accurately weigh 0.15g(accurate to 0.0001g) of potassium hydrogen phthalate reference reagent, place it in a dry titration cup, add 50mL of glacial acetic acid solution, warm and stir until it is completely dissolved, place it on the stirring table, insert the electrode, titrate with perchloric acid titration solution until the potential suddenly crosses the endpoint, record the titration volume, and repeat three times. Meanwhile, conduct the blank titration experiment. Calculate the concentration of the titration solution.
(2) Accurately weigh 0.25g of the sample (accurate to 0.0001g) and place it in a dry titration cup. Add 3mL of formic acid and 50
mL glacial acetic acid, start stirring for 20 seconds to ensure complete dissolution of the sample, insert the electrode, start the prepared method, and titrate with the calibrated perchloric acid titration solution until the potential leap endpoint is reached. Record the titration volume, repeat this process three times, and simultaneously create a blank volume.
3.2 Parameter Settings
| Titration mode: Dynamic titration | Stirring speed: 6 | ||
| Electrode equilibrium time: 4 seconds | Pre-stirring time: 1 second | ||
| Electrode equilibrium potential: 1mv | liquid replenishment rate: 7 | ||
| Minimum addition volume: 0.02mL. | Pre-titration addition volume: 0mL | ||
| Final volume: 10mL. | Stirring time after pre-titration: 1 second | ||
| Potential leap: 300 | Pre-controlled mv value: None |
4 Results and Discussion
4.1 Experimental Results
|
Sample name |
sample number | titrant concentration (mol/L) | (g ) sampling quantity | titration volume V1 (mL) | blank volume where V0 (mL) | content (%) | average (%) |
RSD(%) |
| Aspatan |
1 |
0.1005 |
0.25245 |
8.224 |
0.06 |
95.650 |
95.592 |
0.114 |
|
2 |
0.25295 |
8.224 |
95.461 |
|||||
|
3 |
0.25485 |
8.303 |
95.666 |
Calculation formula:
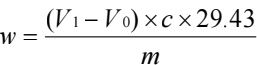
In the formula:
m is the mass of the sample to be weighed;
V1 is the amount of titrant consumed;
V0 is the blank volume;
29.43 is the mass of C14H18N2O50 corresponding to 0.1 mol/L perchloric acid titrant, with the unit of mg
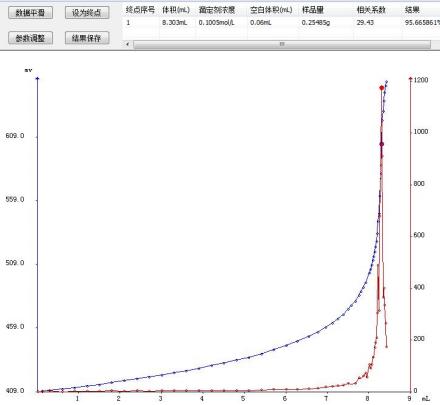
4.2 Atlas
4.3 Conclusion
The determination of the content of aspartan by the JH-T7 fully automatic potentiometric titrator has good repeatability. The determination results are all within its standard range, and the RSD is ≤0.5%. The T960 fully automatic potentiometric titrator fully meets the determination requirements of this sample.


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
+86 15021993094
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight July 2025
Pharma Sources Insight July 2025


